EMI shielding tapes and films refer to the use of a shielding layer (a formed conductive material) to partially or completely enclose an electronic circuit, which restricts the amount of EMI radiation that can penetrate the circuit from the external environment. Likewise, it also limits the impact of EMI energy generated by the circuit on the external environment.
The shielding layer is altered by absorbing or reflecting electromagnetic waves through conductive or ferromagnetic materials. When it comes to EMI shielding, there are three different mechanisms:
- The primary mechanism of EMI shielding is reflection, which attenuates the EMI component. In this mechanism, the higher the electrical conductivity of the material, the better the shielding properties.
- Absorption is the secondary mechanism of EMI shielding. To achieve absorption, the material must have electric and magnetic dipoles, which are materials with high dielectric constants and high magnetic permeability.
- Multiple reflections are another mechanism observed in shielding laminates with large interface areas or porous structures. Shielding is achieved by reflecting electromagnetic waves through multiple reflection boundaries, resulting in the scattering of electromagnetic waves.
Effective EMI shielding materials
Effective EMI shielding materials require good electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability. Common materials used for electromagnetic shielding include metals, carbon-based composites, intrinsically conducing polymers, silicone, foams, films, and fabrics, among others.
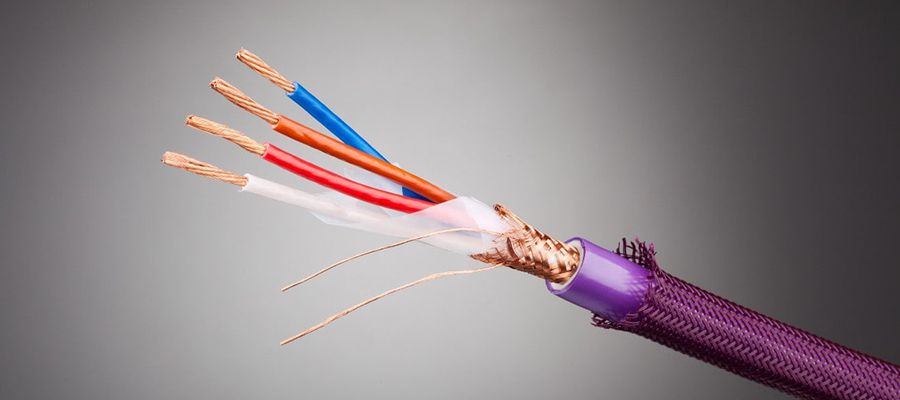
EMI Shielding Tapes - Cable Shielding
These are tapes or films covering insulated conductors of power or instrument cables. When used on power lines, this prevents electromagnetic waves from affecting nearby electronic components. When used for instrument wiring, the primary function is to prevent external electromagnetic waves from distorting the signals flowing through the cable. The shielding layer is grounded to ensure that any current or stored energy leaking through parasitic capacitance is transferred to the ground.
Product Shielding Performances
- Low Frequency: 30~1500 Hz, shielding values range from 40~80 dB.
- High Frequency: 1~20 GHz, shielding values range from 45~78 dB.
Customization
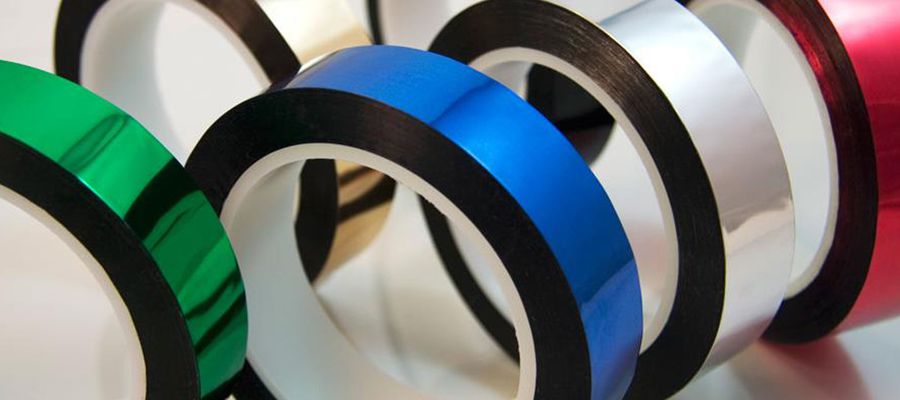
- Optional non-metal materials: PEN, PET, PPS, PP, PI, PTFE, EPTFE.
- Optional metal materials: aluminum, copper, gold, silver, nickel, tin, indium, etc.
- Processing techniques: laminating and vacuum metalizing.
Shielding laminates
Vacuum metallized films & fabrics