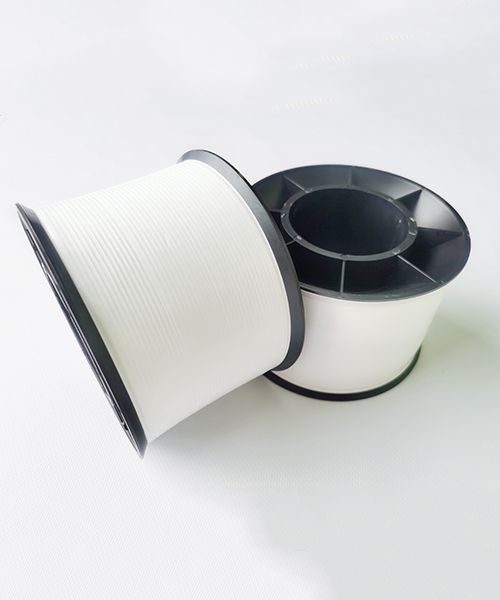
- Total thickness: (10μm to over 100μm) ±3μm
- PET layer thickness: (≥1.6μm) + aluminum layer (≥0.1μm)
- Tensile strength: ≥30Mpa
- Width: 0.5mm to 990mm
- Elongation rate: ≥30% minimum
- Packaging: rolls(D30), sheets, 76mm removable rolls, inverted cone packaging
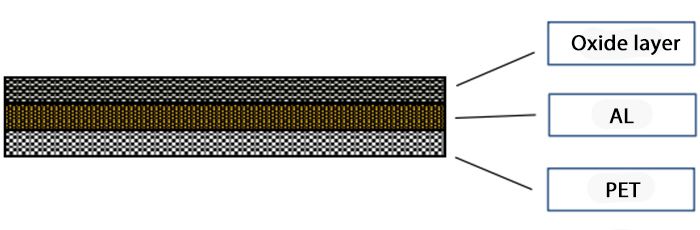
Aluminum metallized PET film involves vacuum depositing aluminum onto the film's surface, which boasts a high dielectric constant, excellent insulation resistance, thermal insulation, and strong tensile properties.
Features
- Suitable for uneven surfaces
- Offers high flexibility
- Easy to use
Applications
- Flame retardant materials
Flame retardant tapes and films employs a flame-retardant backing, preventing contact between flammable substances (such as motor oil, lubricants, etc.) and high-temperature components, thereby reducing the risk of fire incidents in vehicles, ships, aircraft, and more. The inner side of the flame-retardant tape typically features pressure-sensitive adhesive, allowing it to wrap around pipes, valves, exhaust systems, turbochargers, etc., ensuring strong adhesion, while the flame-resistant backing on the reverse side enhances flame-retardant and insulation capabilities. - Thermal conductive materials
Insulation tape for sealing joints in pipes and ventilation ducts, preventing energy and heat loss, and improving energy efficiency.
EMI shielding tape for reducing EMI interference in electronic products.
Pipeline protection tape for safeguarding pipes against corrosion, wear, or damage. - Data transmission cable
Total Thickness: (10μm to over 100μm) ±3μm
Non-Metal Base Layer Thickness: (≥1.6μm)
Metal Layer Thickness: (≥0.1μm)
Tensile Strength: ≥30Mpa
Width: 0.5mm to 990mm
Elongation Rate: ≥30% Min
Heat Sealing Strength: 3.5KG - EMI shielding
Effective EMI shielding materials require good electrical conductivity and magnetic permeability. Common materials used for electromagnetic shielding include metals, carbon-based composites, intrinsically conducing polymers, silicone, foams, films, and fabrics, among others.
What is vacuum metallization?
Vacuum metallization encompasses methods like vacuum deposition, sputtering, and ion plating, which create various metal and non-metal films on product surfaces within a vacuum environment, achieving the effect of plating.
How does vacuum metallization differ from electroplating?
The main difference between electroplating and vacuum metallization is the cost. Vacuum metallization is generally more expensive, and its process complexity is higher compared to electroplating.
What are the cable taping methods?
Cable taping methods include longitudinal taping and cross taping. Cross taping further divides into traverse taping and diagonal taping. Longitudinal taping is used for core wires where no overall stranding is required, and it does not require flexibility. Traverse taping is a high-speed process with good flexibility.
What Is the primary use of copper/PET shielding tapes?
Copper/PET shielding tapes is primarily used in various fields, such as extremely fine coaxial wires, low-loss antennas (computers), solar cell wires, etc.
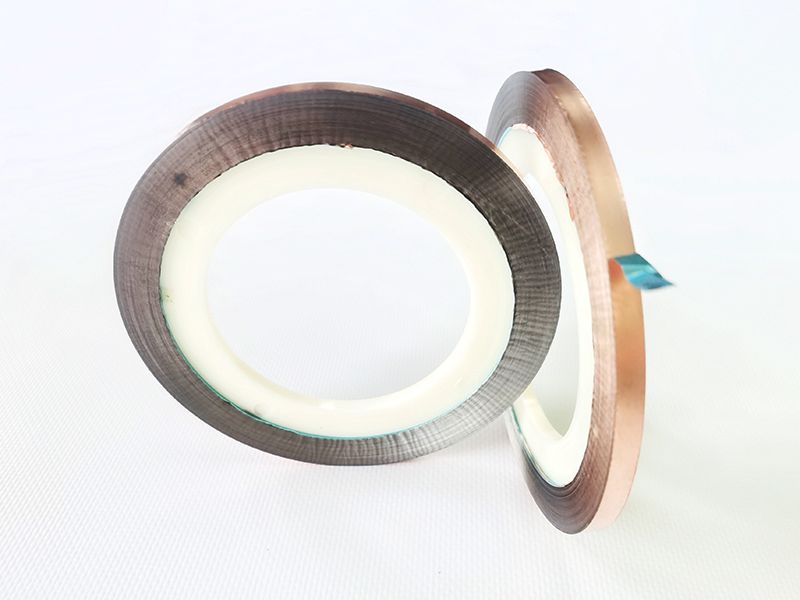










 Polyester Film Tape (PET Tape)
Polyester Film Tape (PET Tape) Shielding Laminates
Shielding Laminates Vacuum Metallized Films & Fabrics
Vacuum Metallized Films & Fabrics