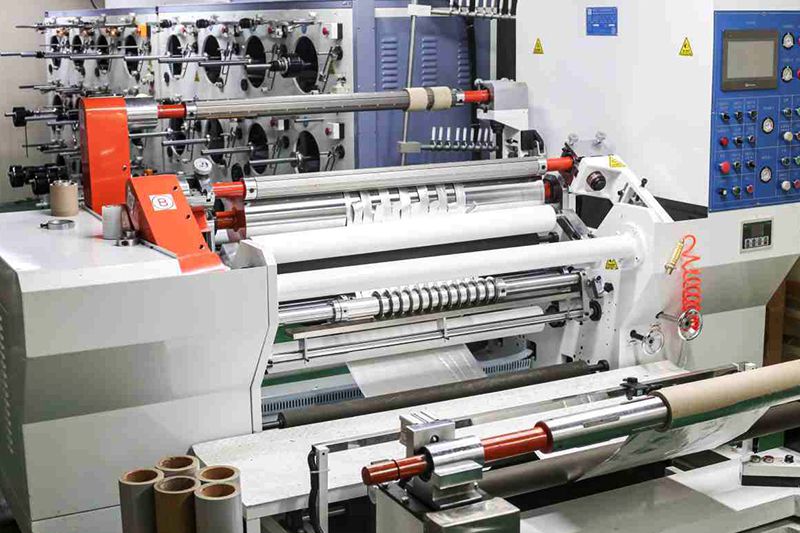
Polyethylene terephthalate (PET), commonly known as polyester resin, is the most prominent type of thermoplastic polyester.
- Total thickness: 4μm to 100μm (±2μm)
- Width: 0.5mm to 990mm (±0.05mm)
- Elongation: ≥25% Minimum
- Tensile strength: ≥80gf (Minimum)
- Heat seal strength: 3KG
- Operating temperature: 70°C to 200°C
- Packaging: rolls(D30), sheets, 76mm removable rolls, inverted cone packaging
- Our PET film has excellent mechanical properties, with an impact strength 3-5 times that of other films and good resistance to folding.
- Resistant to oils, fats, weak acids, and alkalis, as well as most solvents.
- Our polyester film tape demonstrates outstanding high and low-temperature resistance, suitable for prolonged use within a temperature range of 120°C, short-term exposure up to 150°C, and can withstand temperatures as low as -70°C, with minimal impact on its mechanical properties during extreme temperature conditions.
- Low gas and water vapor permeability, providing excellent barrier properties against air, water, oil, and odors.
- Our polyester film tape presents high transparency, capable of blocking ultraviolet rays and displaying good gloss.
- Non-toxic, odorless, and hygienically safe, making our polyester film tapes suitable for direct use in food packaging.
- Ultra-fine flexible wire
EMI solutions include three main approaches: electromagnetic interference shielding, printed circuit board grounding, and electromagnetic interference absorption.
- Electromagnetic Interference Shielding involves blocking electromagnetic noise and attenuating cable-collected noise. It uses high-reflectance materials (usually low-resistance metals) to encase or seal openings in target devices for EMI and EMS solutions.
- Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Grounding refers to grounding electronic equipment electrically to prevent electric shock, treating the Earth as a massive conductor at zero electric potential. Two grounding methods are employed: frame grounding and signal grounding on PCBs.
- Electromagnetic Interference Absorption (EMI Absorption) utilizes magnetic loss, dielectric loss, and conduction loss to convert radio wave energy into thermal energy. EMI absorbers have a wide range of applications.
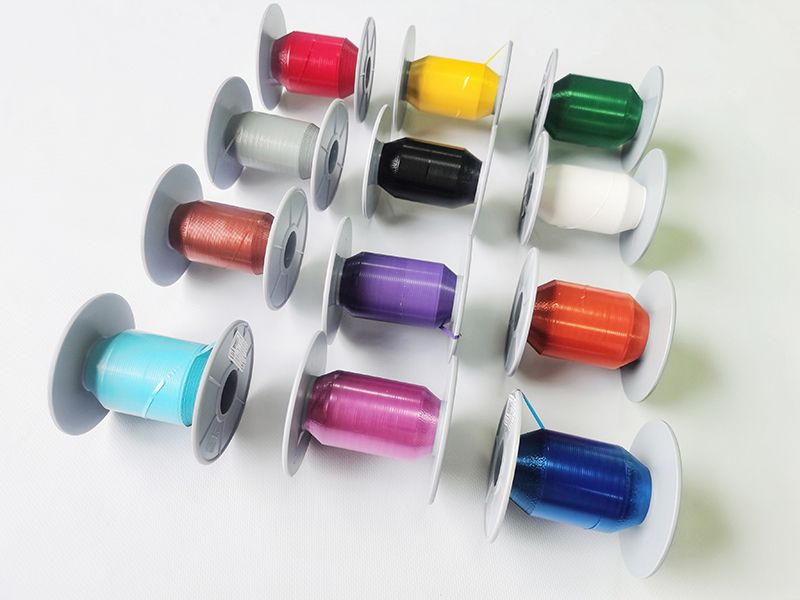





 Polyester Film Tape (PET Tape)
Polyester Film Tape (PET Tape) Shielding Laminates
Shielding Laminates Vacuum Metallized Films & Fabrics
Vacuum Metallized Films & Fabrics